This notebook is an exercise in the Computer Vision course. You can reference the tutorial at this link.
Introduction
简介
In these exercises, you'll explore what effect various random transformations have on an image, consider what kind of augmentation might be appropriate on a given dataset, and then use data augmentation with the Car or Truck dataset to train a custom network.
在这些练习中,您将探索各种随机变换对图像的影响,考虑哪种增强可能适合给定的数据集,然后使用数据增强和 Car or Truck 数据集来训练自定义网络。
Run the cell below to set everything up!
运行下面的单元格以设置所有内容!
# Setup feedback system
from learntools.core import binder
binder.bind(globals())
from learntools.computer_vision.ex6 import *
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras.layers.experimental import preprocessing
# Imports
import os, warnings
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import gridspec
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image_dataset_from_directory
# Reproducability
def set_seed(seed=31415):
np.random.seed(seed)
tf.random.set_seed(seed)
os.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = str(seed)
#os.environ['TF_DETERMINISTIC_OPS'] = '1'
set_seed()
# Set Matplotlib defaults
plt.rc('figure', autolayout=True)
plt.rc('axes', labelweight='bold', labelsize='large',
titleweight='bold', titlesize=18, titlepad=10)
plt.rc('image', cmap='magma')
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # to clean up output cells
# Load training and validation sets
ds_train_ = image_dataset_from_directory(
'../input/car-or-truck/train',
labels='inferred',
label_mode='binary',
image_size=[128, 128],
interpolation='nearest',
batch_size=64,
shuffle=True,
)
ds_valid_ = image_dataset_from_directory(
'../input/car-or-truck/valid',
labels='inferred',
label_mode='binary',
image_size=[128, 128],
interpolation='nearest',
batch_size=64,
shuffle=False,
)
# Data Pipeline
def convert_to_float(image, label):
image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype=tf.float32)
return image, label
AUTOTUNE = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
ds_train = (
ds_train_
.map(convert_to_float)
.cache()
.prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
)
ds_valid = (
ds_valid_
.map(convert_to_float)
.cache()
.prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
)
2024-08-30 07:18:34.444985: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:9261] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered
2024-08-30 07:18:34.445038: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:607] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered
2024-08-30 07:18:34.446562: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1515] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
Found 5117 files belonging to 2 classes.
Found 5051 files belonging to 2 classes.(Optional) Explore Augmentation
(可选)探索增强
Uncomment a transformation and run the cell to see what it does. You can experiment with the parameter values too, if you like. (The factor parameters should be greater than 0 and, generally, less than 1.) Run the cell again if you'd like to get a new random image.
取消注释转换并运行单元格以查看其作用。如果愿意,您也可以尝试参数值。(因子参数应大于 0,通常小于 1。)如果您想获取新的随机图像,请再次运行单元格。
# all of the "factor" parameters indicate a percent-change
augment = keras.Sequential([
preprocessing.RandomContrast(factor=0.5),
preprocessing.RandomFlip(mode='horizontal'), # meaning, left-to-right
preprocessing.RandomFlip(mode='vertical'), # meaning, top-to-bottom
preprocessing.RandomWidth(factor=0.15), # horizontal stretch
preprocessing.RandomRotation(factor=0.20),
preprocessing.RandomTranslation(height_factor=0.1, width_factor=0.1),
])
ex = next(iter(ds_train.unbatch().map(lambda x, y: x).batch(1)))
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(16):
image = augment(ex, training=True)
plt.subplot(4, 4, i+1)
plt.imshow(tf.squeeze(image))
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()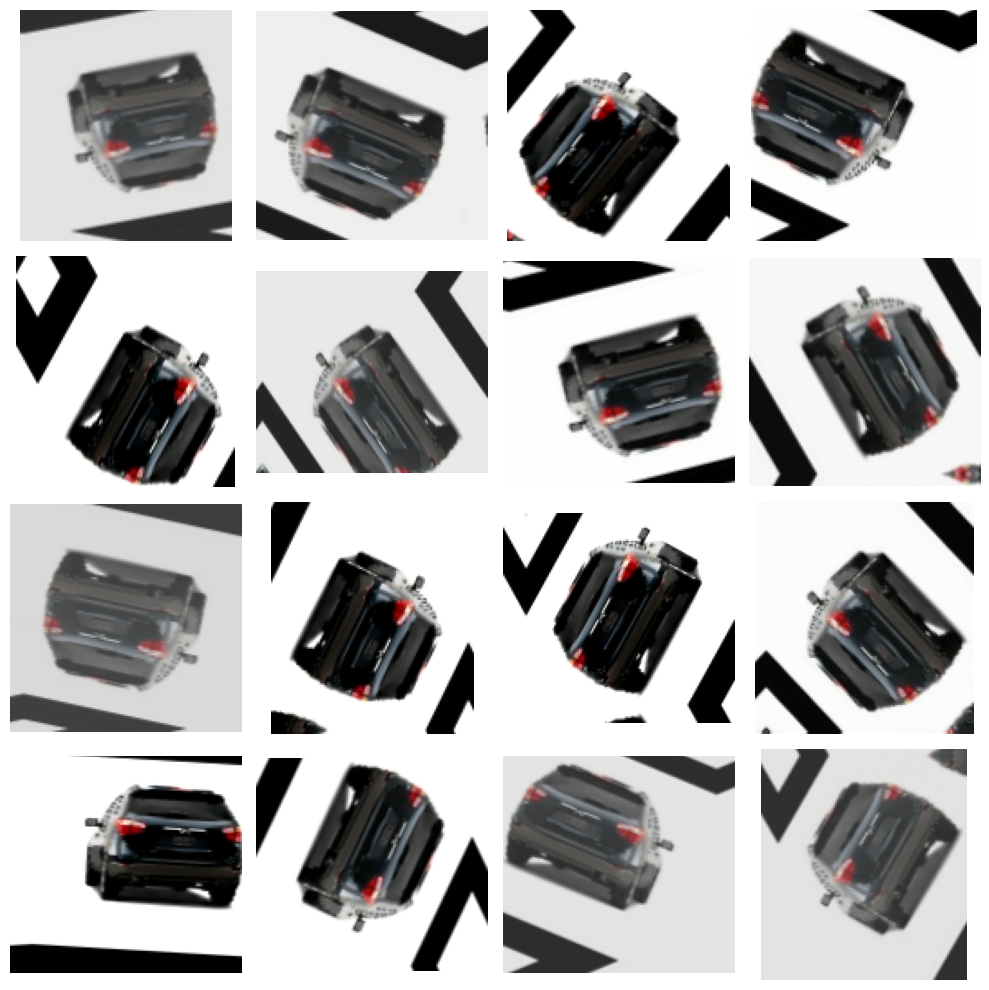
Do the transformations you chose seem reasonable for the Car or Truck dataset?
您选择的转换对于汽车或卡车数据集来说是否合理?
In this exercise, we'll look at a few datasets and think about what kind of augmentation might be appropriate. Your reasoning might be different that what we discuss in the solution. That's okay. The point of these problems is just to think about how a transformation might interact with a classification problem -- for better or worse.
在本练习中,我们将查看一些数据集并思考哪种增强可能是合适的。您的推理可能与我们在解决方案中讨论的不同。没关系。这些问题的目的只是思考转换如何与分类问题相互作用——无论是好是坏。
The EuroSAT dataset consists of satellite images of the Earth classified by geographic feature. Below are a number of images from this dataset.
EuroSAT 数据集由按地理特征分类的地球卫星图像组成。以下是该数据集中的一些图像。
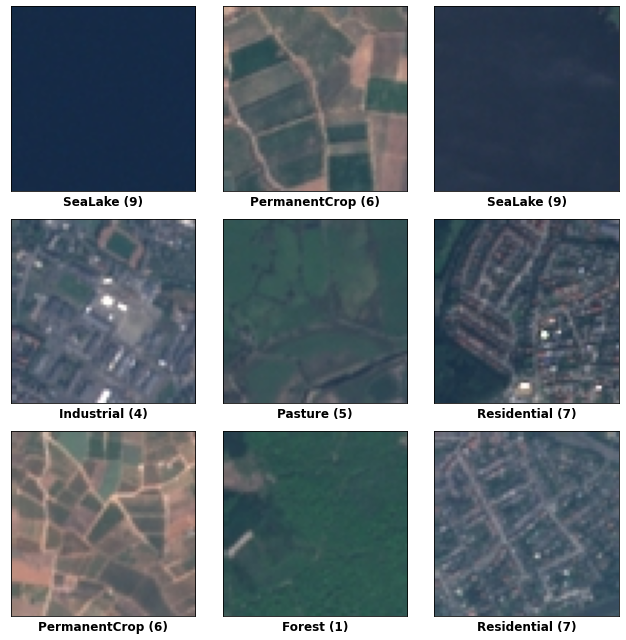

1) EuroSAT
What kinds of transformations might be appropriate for this dataset?
哪些类型的转换可能适合该数据集?
# View the solution (Run this code cell to receive credit!)
q_1.check()Correct:
It seems to this author that flips and rotations would be worth trying first since there's no concept of orientation for pictures taken straight overhead. None of the transformations seem likely to confuse classes, however.
在我看来,翻转和旋转是值得首先尝试的,因为对于从头顶直接拍摄的照片,没有方向的概念。然而,这些变换似乎都不太可能混淆类别。
# Lines below will give you a hint
# q_1.solution()The TensorFlow Flowers dataset consists of photographs of flowers of several species. Below is a sample.
TensorFlow Flowers 数据集包含多个品种的花卉照片。以下是样本。

2) TensorFlow Flowers
2) TensorFlow Flowers
What kinds of transformations might be appropriate for the TensorFlow Flowers dataset?
哪些类型的转换可能适合 TensorFlow Flowers 数据集?
# View the solution (Run this code cell to receive credit!)
q_2.check()Correct:
It seems to this author that horizontal flips and moderate rotations would be worth trying first. Some augmentation libraries include transformations of hue (like red to blue). Since the color of a flower seems distinctive of its class, a change of hue might be less successful. On the other hand, there is suprising variety in cultivated flowers like roses, so, depending on the dataset, this might be an improvement after all!
作者认为水平翻转和适度旋转是值得首先尝试的。一些增强库包括色调转换(如从红色到蓝色)。由于花朵的颜色似乎与其类别不同,因此色调的改变可能不太成功。另一方面,玫瑰等栽培花卉的种类令人惊讶,因此,根据数据集,这可能毕竟是一种改进!
# Lines below will give you a hint
# q_2.solution()Now you'll use data augmentation with a custom convnet similar to the one you built in Exercise 5. Since data augmentation effectively increases the size of the dataset, we can increase the capacity of the model in turn without as much risk of overfitting.
现在,您将使用类似于在练习 5 中构建的自定义卷积网络进行数据增强。由于数据增强有效地增加了数据集的大小,我们可以反过来增加模型的容量,而不会产生过度拟合的风险。
3) Add Preprocessing Layers
3) 添加预处理层
Add these preprocessing layers to the given model.
将这些预处理层添加到给定的模型中。
preprocessing.RandomContrast(factor=0.10),
preprocessing.RandomFlip(mode='horizontal'),
preprocessing.RandomRotation(factor=0.10),from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
model = keras.Sequential([
layers.InputLayer(input_shape=[128, 128, 3]),
# Data Augmentation
# ____,
preprocessing.RandomContrast(factor=0.10),
preprocessing.RandomFlip(mode='horizontal'),
preprocessing.RandomRotation(factor=0.10),
# Block One
layers.BatchNormalization(renorm=True),
layers.Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.MaxPool2D(),
# Block Two
layers.BatchNormalization(renorm=True),
layers.Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=3, activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.MaxPool2D(),
# Block Three
layers.BatchNormalization(renorm=True),
layers.Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=3, activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size=3, activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.MaxPool2D(),
# Head
layers.BatchNormalization(renorm=True),
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(8, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'),
])
# Check your answer
q_3.check()Correct
# Lines below will give you a hint or solution code
#q_3.hint()
#q_3.solution()Now we'll train the model. Run the next cell to compile it with a loss and accuracy metric and fit it to the training set.
现在我们将训练模型。运行下一个单元,使用损失和准确度指标对其进行编译,并将其拟合到训练集。
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(epsilon=0.01)
model.compile(
optimizer=optimizer,
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['binary_accuracy'],
)
history = model.fit(
ds_train,
validation_data=ds_valid,
epochs=50,
verbose=False,
)
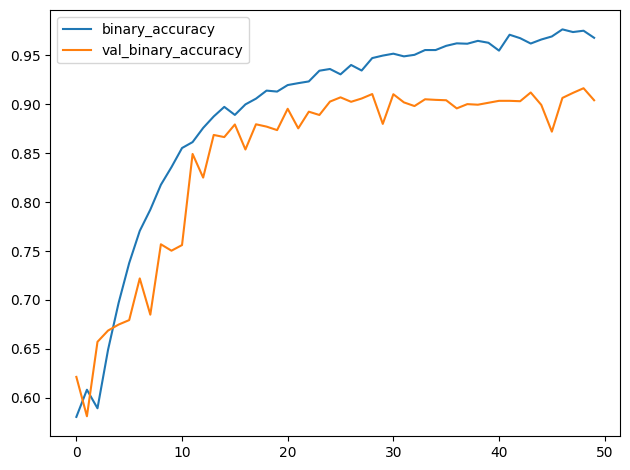
# Plot learning curves
import pandas as pd
history_frame = pd.DataFrame(history.history)
history_frame.loc[:, ['loss', 'val_loss']].plot()
history_frame.loc[:, ['binary_accuracy', 'val_binary_accuracy']].plot();WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR
I0000 00:00:1725002331.932419 1475 device_compiler.h:186] Compiled cluster using XLA! This line is logged at most once for the lifetime of the process.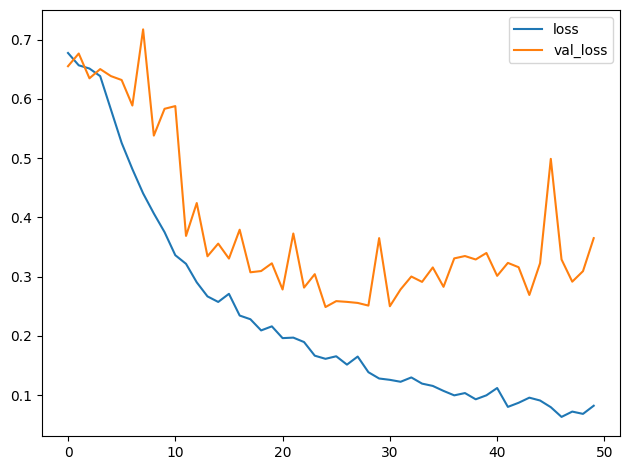
4) Train Model
4) 训练模型
Examine the training curves. What there any sign of overfitting? How does the performance of this model compare to other models you've trained in this course?
检查训练曲线。有没有过度拟合的迹象?与你在本课程中训练过的其他模型相比,该模型的性能如何?
# View the solution (Run this code cell to receive credit!)
q_4.solution()Solution:
The learning curves in this model stayed close together for much longer than in previous models. This suggests that the augmentation helped prevent overfitting, allowing the model to continue improving.
And notice that this model achieved the highest accuracy of all the models in the course! This won't always be the case, but it shows that a well-designed custom convnet can sometimes perform as well or better than a much larger pretrained model. Depending on your application, having a smaller model (which requires fewer resources) could be a big advantage.
与之前的模型相比,此模型的学习曲线保持紧密的时间更长。这表明增强有助于防止过度拟合,从而使模型继续改进。
请注意,此模型的准确率是本课程中所有模型中最高的!情况并非总是如此,但它表明,精心设计的自定义卷积网络有时可以表现得与更大的预训练模型一样好甚至更好。根据您的应用程序,拥有较小的模型(需要更少的资源)可能是一个很大的优势。
Conclusion
结论
Data augmentation is a powerful and commonly-used tool to improve model training, not only for convolutional networks, but for many other kinds of neural network models as well. Whatever your problem, the principle remains the same: you can make up for an inadequacy in your data by adding in "fake" data to cover it over. Experimenting with augmentations is a great way to find out just how far your data can go!
数据增强是一种强大且常用的工具,可以改善模型训练,不仅适用于卷积网络,也适用于许多其他类型的神经网络模型。无论您遇到什么问题,原理都是一样的:您可以通过添加“假”数据来弥补数据的不足。尝试增强是一种很好的方法,可以找出您的数据可以走多远!
The End
最后
That's all for Computer Vision on Kaggle Learn! Are you ready to apply your knowledge? Check out our two bonus lessons! They'll walk you through preparing a submission for a competition while you learn how to train neural nets with TPUs, Kaggle's most advanced accelerator. At the end, you'll have a complete notebook ready to extend with ideas of your own.
以上就是 Kaggle Learn 上的 计算机视觉 的全部内容!您准备好应用您的知识了吗?查看我们的两个奖励课程!它们将指导您准备竞赛提交内容,同时您将学习如何使用 TPU(Kaggle 最先进的加速器)训练神经网络。最后,您将拥有一个完整的笔记本,随时可以扩展自己的想法。
- Create Your First Submission - Prepare a submission for our Petals to the Metal Getting Started competition. You'll train a neural net to recognize over 100 species of flowers.
- 创建您的第一个提交内容 - 为我们的 Petals to the Metal 入门竞赛准备提交内容。您将训练一个神经网络来识别 100 多种花卉。
- Cassava Leaf Disease - Rather compete for money and medals? Train a neural net to diagnose common diseases in the cassava plant, a staple security crop in Africa.
- 木薯叶病 - 宁愿争夺金钱和奖牌?训练神经网络来诊断木薯(非洲的主要安全作物)的常见疾病。
Have fun learning!
祝您学习愉快!